Difference between revisions of "Speed"
m |
m |
||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
===If nothing works=== | ===If nothing works=== | ||
If none of these hints manages to resolve unexplained slow speed, then your next step should be to read [[Troubleshooting | If none of these hints manages to resolve unexplained slow speed, then your next step should be to read [[Troubleshooting]]. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[NCF DSL Rates]] | *[[NCF DSL Rates]] | ||
*[[Line | *[[Line Stats]] | ||
*[[Troubleshooting | *[[Troubleshooting]] | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Revision as of 01:11, 28 July 2018
DSL service is provided to NCF members with an "up to" speed for both download and upload. This means that it can be less than that speed, for reasons that are out of NCF's control.
There are a myriad of factors that affect the actual speed of your DSL connection. This article will attempt to address the main ones.
How much speed are you getting?
Don't rely on subjective appraisals that some websites are loading slowly to determine that your speed is slow. It is very common that the speed limiter is the server at the other end. For instance, news video websites can be very slow in the evenings, because many people are trying to download the videos all at once.
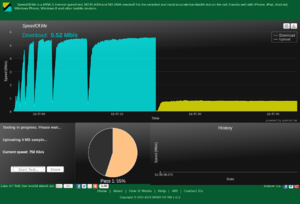
Your achieved DSL speed should be objectively measured, which is easy to do. There are two speeds that are relevant:
- Your line profile speed, which your modem detects and records in its line stats. Line stats (DSL) shows you how to find out what your modem records the line profile as.
- Your actual achieved speed, though running a speed test.
Line profile speeds
Why would your line profile be set below the maximum? Because your distance from Bell's DSL equipment or the quality of Bell's lines to your house cannot support a higher speed. DSL signal degrades with distance from the DSL equipment and distances over 5 km tend to be very marginal for DSL signals. Even shorter distances can result in service instability and loss of connection at higher speeds. The cure for this is to slow down the speed to prevent disconnections.
You can get some idea of your distance from the DSL equipment and whether distance is an issue for your location, by checking your line attenuation. If the attenuation is high then you are far from the DSL equipment and a lower profile is probably called for to prevent frequent disconnections.
You can see your stats as seen by NCF here. Note the date on that page that says when they were collected.
Achieved Speeds
Why don't speed test results match the profile?
You will rarely see your profile speed as a download speed on a speed test. There is a service "overhead" on all DSL speeds that means that achieved speeds are usually limited to about 85% of the profile speed. If you have a 10 Mb/s download profile speed this will mean ideally you should see speed tests turn in results of about 8.5 Mb/s. Similarly with upload speeds on a profile of 800 Kb/s upload profile expect to see the speed test turning in a result of 680 Kb/s.
How to do a speed test
To find the speed of your DSL connection, try a speed test website and and click on 'Begin test'. It will time how long it takes to download and upload test files to their site to tell you the speed of your connection.
A proper test of your connection should use an Ethernet wired connection. If you test both Ethernet and Wi-Fi and find a difference in speed then that is due to the losses and interference involved in Wi-Fi. For more information see about wireless.
It is normal for the download speed to be much faster than the upload speed. This is intentional, so that you are able to download big files quickly.
Normal, good results for 6 Mbps service would be something like 5.2 Mbps download, and about 600 Kbps upload.
If your results are not as good as you would expect, try asking your neighbours what speeds they are getting. That will give you an indication of how well your neighbourhood is being served by Bell. If your speeds are slower than your neighbours then check Troubleshooting (DSL) for ideas on what to check to improve your DSL performance.
Speed tests:
- NCF Internet Speed Test (HTML5 test - does not require Adobe Flash or Java, but will require a modern browser that can use HTML5))
- NCF Second Internet Speed Test (HTML5 test - does not require Adobe Flash or Java, but will require a modern browser that can use HTML5))
- Speedtest.net (requires Adobe Flash)
- Speedtest.net - beta HTML5 version (does not require Adobe Flash)
- Primus Internet Speed Test (requires Adobe Flash)
- SpeakEasy Speed Test (requires Adobe Flash)
- TechSavvy Speed Test (requires Adobe Flash)
- Meter.net Speed Test (HTML5 test - does not require Adobe Flash or Java, but will require a modern browser that can use HTML5)
- Speed of Me Speed Test (HTML5 test - does not require Adobe Flash or Java, but will require a modern browser that can use HTML5)
- Bandwidth Place Speed Test (HTML5 test - does not require Adobe Flash or Java, but will require a modern browser that can use HTML5)
- Cira .CA Performance Test (HTML5 test - does not require Adobe Flash or Java, but will require a modern browser that can use HTML5)
- Netflix-operated Speed Test (HTML5 test - does not require Adobe Flash or Java, download-only)
Note: Because different test servers are located in different geographical places their results will not be comparable to each other and testing the same DSL connection on different speed tests will give different results. If you use a speed test to monitor your connection over time, then always use the same test.
What if the speed test shows slow speed?
If you are on a profile of 10 Mb/s and you are seeing speed test results over 8 Mb/s in real world conditions that is normal. If you are getting download speeds in the range of 5 Mb/s or slower then that may indicate a problem.
It could be due to any one of a number of problems:
Network congestion
If you get expected speeds in the morning and late at night, but experience slower speeds in the evenings and on weekends then the likely culprit is network congestion. NCF has investigated network congestion problems in the past and correct issues between the NCF network and the Bell Network at the aggregation point.
Today NCF increases its bandwidth on regular basis to stay ahead member demand, but slowdowns still occur on the internet beyond NCF, as this article explains.
Other users
When you did the speed test were you the only person using your internet connection? If someone else in the house is watching a video, streaming audio or is playing a game, it will consume bandwidth and give you a slow speed test result. Try retesting when you are sure no one else is on line through your modem.
Are you running your wireless unencrypted? Are people outside your home using your bandwidth? Running your wireless unencrypted is not recommended.
Wireless
Speeds seen when speed testing via wireless connection are almost always slower than via wired Ethernet connection, unless the device connected wirelessly is very close to the router. Even with an "N" protocol wireless router a laptop being used for a speed test a floor above the router will typically see half the expected speeds. With "G" protocol wireless it may be one quarter the expected speed, or worse, if there is interference from other nearby networks.
If you are not getting good speed on your wirelessly connected device then try connecting it via an Ethernet cable and see if that makes a difference. See About WiFi for more information on troubleshooting WiFi performance
Modem
Any modem should give comparable speeds on the same line, unless the modem is starting to fail. One possible sign of a failing modem is loss of speed, especially once it is warmed up and has been running for an hour or two.
Poor ventilation for a modem can cause it to overheat and lose speed, so ensure that your modem has good airflow around it.
If you suspect your modem may be the issue contact the NCF office to arrange to borrow a loaner modem to take home and test out your connection.
Browser
Running a speed test on an old browser will often turn in slow results, because the browser is slow. Make sure you have the latest version of your browser to ensure that the speed test is not being limited.
Some browsers don't necessarily work well or fast and can produce slow results, particularly some versions of Microsoft Internet Explorer. Try a better browser:
- Apple Safari for macOS
- Brave for Linux, macOS, and Windows
- Chromium for BSD and Linux
- Gnome Web (formerly called "Epiphany") for Linux
- Google Chrome for BSD, Linux, macOS, and Windows
- Midori for BSD, Linux and Windows
- Mozilla Firefox for BSD, Linux, macOS, and Windows
- Mozilla SeaMonkey for BSD, Linux, macOS, and Windows
- SRWare Iron for BSD, Linux, macOS, and Windows
- Vivaldi for Linux, macOS, and Windows
Operating system
An operating system on your computer that has errors and is breaking down and malfunctioning will not give good speed test results. Microsoft Windows, in particular, breaks down over time and can turn in poor results.
This can easily be tested by running a speed test on another computer and seeing if the results are different, or booting up another operating system and testing using that. A simple, RAM-based operating system, like Puppy Linux is easy to boot into RAM and, with its included Firefox browser, conduct a speed test. If the result is faster than normal, then the operating system is probably the culprit.
Computer hardware
It is also possible that your computer's network or wireless card is failing and producing slow speeds. The easiest way to test this is by using another device to conduct a speed test and then compare the results. Different computers connecting the same way and using the same speed test should see similar results.
If nothing works
If none of these hints manages to resolve unexplained slow speed, then your next step should be to read Troubleshooting.
See also
External links
- The bandwidth bottleneck that is throttling the Internet, by Jeff Hecht, Nature
