Port forwarding
Port forwarding allows you to sign into a local computer network from outside, via the internet and carry out tasks on the network, such as editing documents, changing configurations or printing.
To accomplish this your DSL modem has to be manually configured to allow port forwarding.
Caution
Port forwarding has distinct security implications and should not be undertaken unless you understand that you are opening your local area network to the open internet. You need to either control access or understand what you have opened access to.
Port forwarding on TP-Link modems
Setting up port forwarding on TP-Link 8816, 8901, 8951, and 8961 model modems is a relatively simple task.
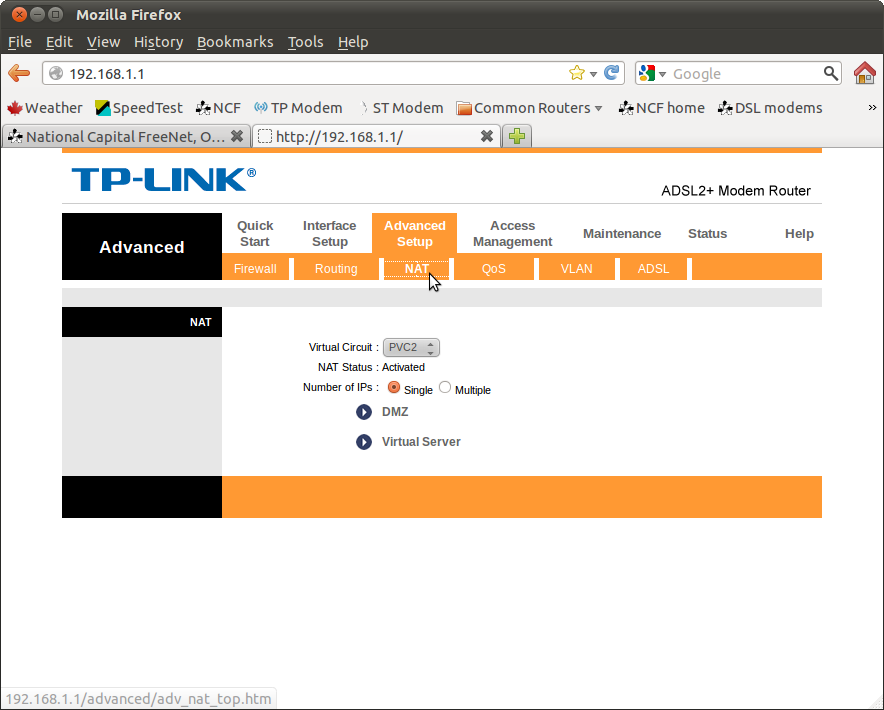
1. Sign into your DSL modem web interface and go to Advanced Setup → NAT.
2. Select a new Virtual Circuit.
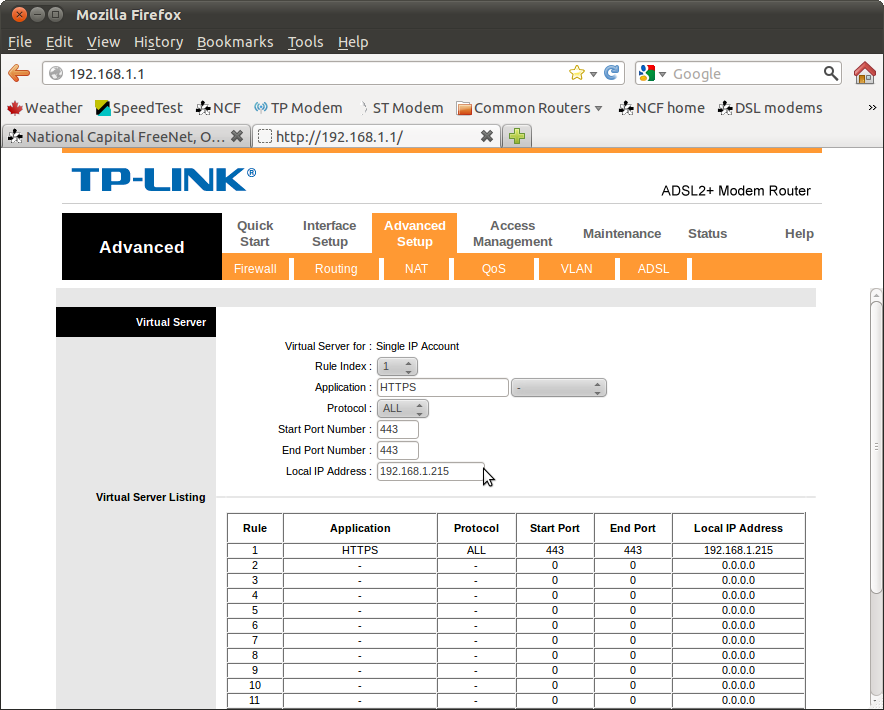
3. Set the rule index to "1" to establish the first rule.
4. Set a name for the application under "Application" (Note: you can choose suggestions from the pull down menu or enter your own name for it manually).
5. Set the port(s) to be opened from "Start port number" and "End port number". (Note: if the same port number is designated under "start" and "end" then only that port will be opened.
6. Set the local IP address of the destination under "Local IP address".
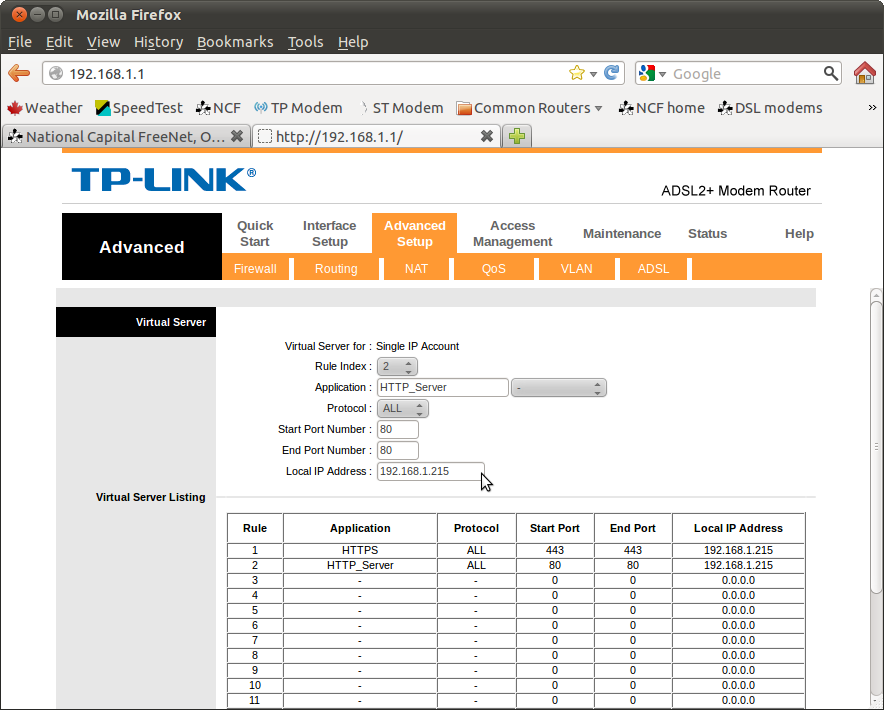
7. Continue to set further rules, if required. These will all appear on the virtual server listing.
Notes:
- The modem will retain these forwards when powered off or when rebooted.
- Rules can be manually edited later to amend them.
- A "factory reset" of the modem to default settings (by putting a pin in the hole on the back of the modem for 20 seconds) will eliminate all port forwards set up.
See also
External links
- More Comprehensive Guide for TD-W8951ND Port Forwarding on PortForward.com
- Port Forwarding on Wikipedia
- Basic explanation of Port Forwarding on Simple English Wikipedia