Difference between revisions of "SpeedTouch 516 and 585 on ADSL2+"
(initial entry) |
m |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In 2009 Bell's infrastructure did not support ADSL2+, while the modems NCF sold then, the Thompson SpeedTouch 516 and 585s did. Because the modems defaulted to ADSL2+ and not the ADSL1 then in use on Bell's networks the modems would not connect. To fix this problem a number of modems shipped at that time were configured to force them into ADSL1 mode, which solved the problem. Now that Bell's infrastructure requires ADSL2+ for 15 | <div class="ncfrightbox"> {{Template:Modem Links}} </div> | ||
In 2009 Bell's infrastructure did not support ADSL2+, while the modems NCF sold then, the Thompson SpeedTouch 516 and 585s, did. Because the modems defaulted to ADSL2+ and not the ADSL1 then in use on Bell's networks the modems would not connect. To fix this problem a number of modems shipped at that time were configured by NCF to force them into ADSL1 mode, which solved the problem. Now that Bell's infrastructure requires ADSL2+ for 15 Mb/s service these modems that were configured that way will not work with 15 Mb/s service unless reconfigured. | |||
The configuration cannot be fixed by doing a factory reset, instead it must be done by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telnet Telnet] into the modem and changing it via command line. Fortunately this is easy to do. | The configuration cannot be fixed by doing a factory reset, instead it must be done by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telnet Telnet] into the modem and changing it via command line. Fortunately this is easy to do. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
==Accessing Telnet== | ==Accessing Telnet== | ||
===Linux and Mac=== | ===Linux and Mac=== | ||
On Linux operating systems you can access telnet by opening a terminal and typing in "telnet 192.168.1. | On Linux operating systems you can access telnet by opening a terminal and typing in "telnet 192.168.1.254" at the prompt. | ||
===Windows=== | ===Windows=== | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
In any version of Windows you can also run telnet by installing and using the [http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/ PuTTY] free software application. | In any version of Windows you can also run telnet by installing and using the [http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/ PuTTY] free software application. | ||
==Configuring the modem for ADSL2+== | ==Configuring the 516 or 585 v7 modem for ADSL2+== | ||
The commands are: | The commands are: | ||
telnet 192.168.1.254 | telnet 192.168.1.254 | ||
User: admin/Administrator | User: admin/Administrator<br /> | ||
Pass: <your dsl password> | Pass: <your dsl password><br /> | ||
xdsl debug multimode config=t1.413issue2+g992.1_annex_a+g992.3_annex_a+g992.3_annex_l+g992.3_annex_m+g992.5_annex_a+g992.5_annex_m | xdsl debug multimode config=t1.413issue2+g992.1_annex_a+g992.3_annex_a+g992.3_annex_l+g992.3_annex_m+g992.5_annex_a+g992.5_annex_m | ||
saveall | saveall | ||
That "xdsl..." is a single command, so in copy and pasting be careful to copy the entire line without any carriage returns, which would compromise the command. | That "xdsl..." is a single command, so in copy and pasting be careful to copy the entire line without any carriage returns, which would compromise the command. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
[[File:Thompson dsl2 fix.png]] | [[File:Thompson dsl2 fix.png]] | ||
== | ==Configuring the 585 v6 modem for ADSL2+== | ||
The commands are: | |||
telnet 192.168.1.254 | |||
User: admin/Administrator<br /> | |||
Pass: <your dsl password><br /> | |||
adsl config xdsltype = adsl2+ | |||
ADSL configuration: | |||
detect-lop = enabled<br /> | |||
syslog = disabled<br /> | |||
and then to confirm: | |||
adsl info | |||
which should return a result similar to: | |||
Modemstate : Up<br /> | |||
xDSL Type : ADSL2+<br /> | |||
Bandwidth (Down/Up - kbit/s) : 15455/797<br /> | |||
Uptime (days hh:mm:ss) : 0 days, 0:01:11 | |||
and then | |||
exit | |||
[[File:Speedtouch v6 dsl2.png]] | |||
[[Category:DSL]] | [[Category:DSL]] | ||
[[Category:Modems]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:45, 28 July 2018
In 2009 Bell's infrastructure did not support ADSL2+, while the modems NCF sold then, the Thompson SpeedTouch 516 and 585s, did. Because the modems defaulted to ADSL2+ and not the ADSL1 then in use on Bell's networks the modems would not connect. To fix this problem a number of modems shipped at that time were configured by NCF to force them into ADSL1 mode, which solved the problem. Now that Bell's infrastructure requires ADSL2+ for 15 Mb/s service these modems that were configured that way will not work with 15 Mb/s service unless reconfigured.
The configuration cannot be fixed by doing a factory reset, instead it must be done by Telnet into the modem and changing it via command line. Fortunately this is easy to do.
Accessing Telnet
Linux and Mac
On Linux operating systems you can access telnet by opening a terminal and typing in "telnet 192.168.1.254" at the prompt.
Windows
On Windows XP and Vista operating systems telnet can be accessed by opening "run" and the "cmd" command and entering telnet.
In Windows 7 and 8 you can bring up the command line by entering "cmd" in the search bar.
In any version of Windows you can also run telnet by installing and using the PuTTY free software application.
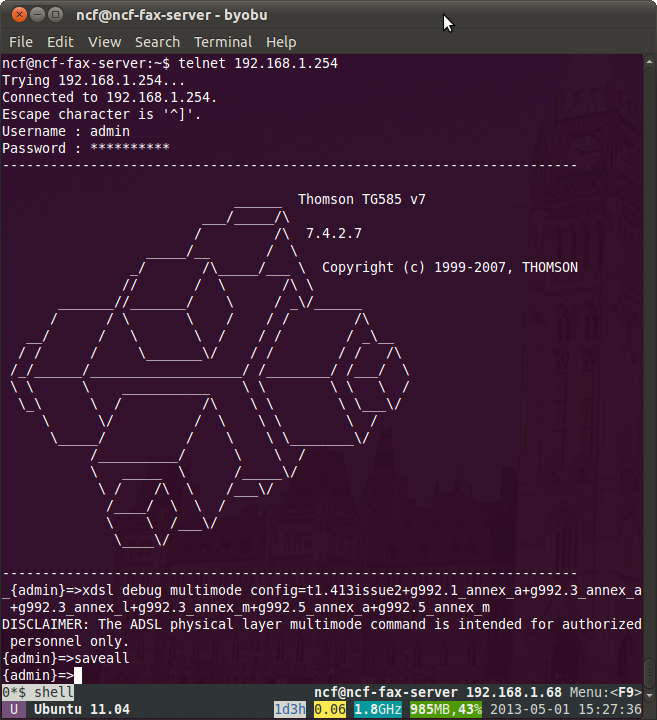
Configuring the 516 or 585 v7 modem for ADSL2+
The commands are:
telnet 192.168.1.254
User: admin/Administrator
Pass: <your dsl password>
xdsl debug multimode config=t1.413issue2+g992.1_annex_a+g992.3_annex_a+g992.3_annex_l+g992.3_annex_m+g992.5_annex_a+g992.5_annex_m
saveall
That "xdsl..." is a single command, so in copy and pasting be careful to copy the entire line without any carriage returns, which would compromise the command.
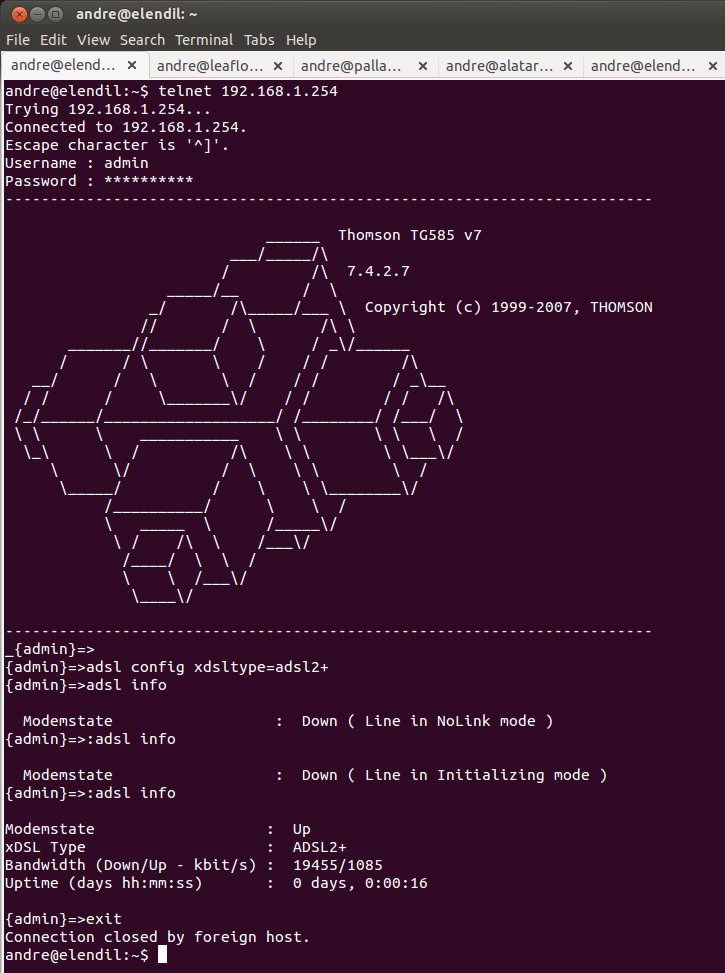
Configuring the 585 v6 modem for ADSL2+
The commands are:
telnet 192.168.1.254
User: admin/Administrator
Pass: <your dsl password>
adsl config xdsltype = adsl2+
ADSL configuration:
detect-lop = enabled
syslog = disabled
and then to confirm:
adsl info
which should return a result similar to:
Modemstate : Up
xDSL Type : ADSL2+
Bandwidth (Down/Up - kbit/s) : 15455/797
Uptime (days hh:mm:ss) : 0 days, 0:01:11
and then
exit